Rifat Tabassoom Tumpa_ARCH655 Final Project
The project was aimed to develop an efficient facade system for buildings in a specific climate to provide enough shading while ensuring necessary daylight in the building floors.
The process was divided into two phases. The 1st phase concerns with the selection of optimized area and location for shading surface and the 2nd phase was focused to develop an efficient shading pattern on the surface.
Phase 1:
For this experiment, a simple cylindrical building was developed with 10 floors. The shading surface was generated from the curvature of the building mass. The area and the location of the shading surface can be changed. Also, the offset distance of the surface from the floors can also be changed.
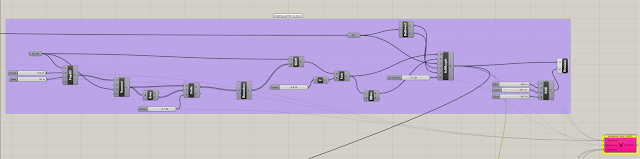
A Genetic Algorithmic tool Galapagos was used for the optimization process. The "Genome" or parameter input is shown in the picture below.
For the "Fitness" or the performance evaluation, the Solar Irradiance (kW/m2) metric was used. The goal was to minimize the irradiance over the building. For this simulation LB Incident Radiation component was used. The tool used the the epw weather file for the location Dhaka, capital city of Bangladesh (23° 48' 39.348'' N).
There were several optimized solutions suggested by Galapagos.
The second optimized option was chosen for next phase considering it as a more ventilated building.
Phase 2:
Simple pattern over the shading surface was considered for this experiment. AI image generation tool DALL.E was used for initial ideas.
The following Voronoi pattern, inspired from one of the AI suggested facades was considered here.
Next, the tool Biomorpher was introduced, which uses Interactive Evolutionary Algorithm (IEAs) to assist designers in the process of evolutionary development. The parameters used here as "Genome" were the seed and count of population points for voronoi diagram, the size of the openings in the pattern and the thickness of the shading surface.
For the "Fitness", the performance evaluation criteria was the Daylight Factor (DF) metric. The DF was calculated by the HB Daylight Factor component.
The settings for the optimization were as following:
K-means clustering is a popular method in data analysis used to partition a set of data points into a specified number of clusters, where each data point belongs to the cluster with the nearest mean. The tool suggests 12 clusters of solutions. From the 1st Generation, DF was asked to be maximized for next generation with preferable solutions to evolve.
To conclude, the script works to find optimized solutions for high-rise facade skin design at the initial phases of design.
















Comments
Post a Comment